Blockchain in Agriculture: Tracing the Food Supply Chain
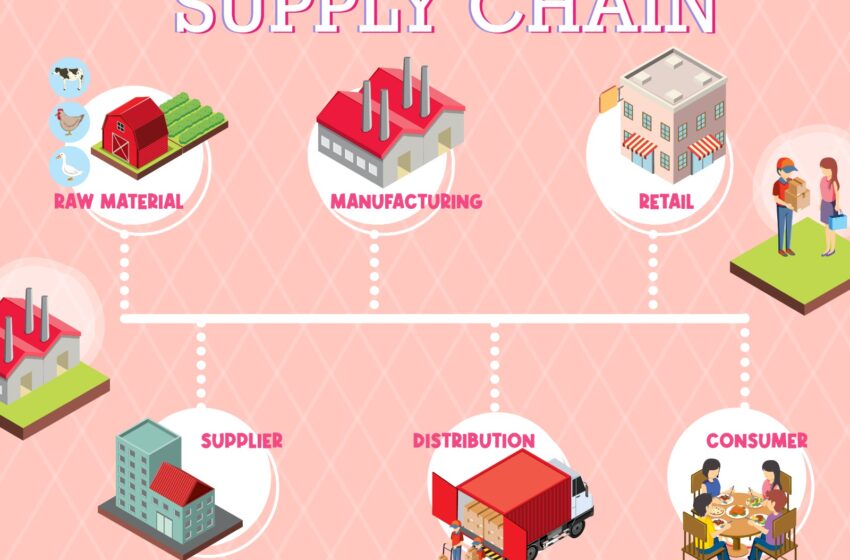
In recent years, blockchain technology has transcended its origins in cryptocurrency to become a revolutionary tool in various sectors, agriculture being one of the most promising. The agriculture industry, the backbone of global food security, faces numerous challenges, including supply chain inefficiencies, food fraud, and the need for sustainability. Blockchain technology offers a compelling solution to these issues by enhancing transparency, traceability, and efficiency in the food supply chain. This article explores the transformative impact of blockchain in agriculture, particularly in tracing the food supply chain, and how it is fostering a more sustainable, secure, and trustworthy food system.
Enhancing Traceability and Transparency
At the heart of blockchain’s appeal is its ability to provide unparalleled traceability and transparency within the food supply chain. By recording every transaction or movement of goods in a tamper-proof ledger, blockchain creates a comprehensive, immutable history of a product’s journey from farm to table. This level of detail not only boosts consumer confidence in the safety and authenticity of food products but also streamlines the process of identifying and addressing issues in the supply chain, such as contamination or counterfeit products.
Combating Food Fraud
Food fraud, a pervasive issue with serious economic and health implications, can be significantly mitigated through blockchain technology. By securely recording each product’s provenance and journey, blockchain makes it virtually impossible for fraudulent products to enter the market undetected. Consumers can access detailed information about the origin, processing, and handling of food products, ensuring authenticity and quality.
Improving Supply Chain Efficiency
Blockchain technology can dramatically improve efficiency within the agriculture supply chain. Traditional supply chain processes often involve a myriad of paperwork, intermediaries, and manual record-keeping, which are time-consuming and prone to errors. Blockchain simplifies these processes by enabling smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Smart contracts automate transactions and agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries and streamlining operations, which can lead to significant cost savings and faster delivery times.
Ensuring Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact and ethical implications of their food choices. Blockchain technology addresses these concerns by providing transparent information about the sustainability practices of producers, including the use of pesticides, water management, and labor practices. This transparency allows consumers to make informed decisions that align with their values, encouraging producers to adopt more sustainable and ethical practices.
Real-world Applications and Success Stories
Several initiatives and companies have successfully implemented blockchain technology in the agriculture sector. For example, IBM’s Food Trust network collaborates with major retailers and suppliers to enhance food traceability across the supply chain. Another example is AgriDigital, which uses blockchain to facilitate secure and transparent transactions between farmers and buyers, ensuring farmers are paid promptly for their produce.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
Despite its potential, the adoption of blockchain in agriculture faces challenges, including the need for technological infrastructure, digital literacy, and widespread industry acceptance. Overcoming these hurdles requires collaboration between technology providers, agricultural businesses, governments, and educational institutions to develop user-friendly platforms and promote the benefits of blockchain technology.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology offers a powerful solution to longstanding challenges in the agriculture sector, particularly in tracing the food supply chain. By enhancing transparency, efficiency, and trust, blockchain has the potential to transform the way we produce, distribute, and consume food. As the technology matures and adoption grows, the future of agriculture looks increasingly secure, sustainable, and interconnected, paving the way for a healthier planet and populace.
(Nominate Now: Join us to spotlight your achievements! Be part of the elite in the business and finance community. Exciting opportunities await!)







